Reflection is a phenomenon in which the wave that strikes a material, returns back to the same medium. The fact that we are able to see ourselves in the mirror is because the light ray that is incident on it, reflects back. Reflection is seen not only in electromagnetic radiations, but also in sound. Echoes are the best example for reflection of sound.
Reflection of light: Refraction of light is of two types. Either specular or diffuse.
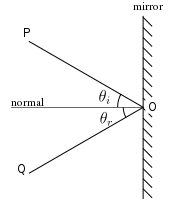
Specular: is the mirror-like reflection of light (or of other kinds of wave) from a surface, in which light from a single incoming direction is reflected into a single outgoing direction. Such behavior is described by the law of reflection, which states that the direction the incident ray), and the direction of the reflected ray make the same angle with respect to the surface normal, thus the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection (θi = θr in the figure), and that the incident, normal, and reflected directions are coplanar.
Laws of Reflection: There are three laws of reflection
Reflection of light: Refraction of light is of two types. Either specular or diffuse.
 |
| Specular |
Specular: is the mirror-like reflection of light (or of other kinds of wave) from a surface, in which light from a single incoming direction is reflected into a single outgoing direction. Such behavior is described by the law of reflection, which states that the direction the incident ray), and the direction of the reflected ray make the same angle with respect to the surface normal, thus the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection (θi = θr in the figure), and that the incident, normal, and reflected directions are coplanar.
Laws of Reflection: There are three laws of reflection
- The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the reflection surface at the point of the incidence lie in the same plane.
- The angle which the incident ray makes with the normal is equal to the angle which the reflected ray makes to the same normal.
- The reflected ray and the incident ray are on the opposite sides of the normal.
Diffuse: is the reflection of light from a surface such that an incident ray is reflected at many angles rather than at just one angle as in the case of specular reflection. An illuminated ideal diffuse reflecting surface will have equal luminance from all directions in the hemisphere surrounding the surface (Lambertian reflectance).
A surface built from a non-absorbing powder such as plaster, or from fibers such as paper, or from a polycrystalline material such as white marble, reflects light diffusely with great efficiency. Many common materials exhibit a mixture of specular and diffuse reflection.The visibility of objects is primarily caused by diffuse reflection of light: it is diffusely-scattered light that forms the image of the object in the observer's eye.








.jpg)



0 comments:
Post a Comment